I have recently been experimenting with Tesseract, an Optical Character Recognition (OCR) engine developed by Google.
My primary objective was to extract text from scans of a 1920s Armenian newspaper and execute search queries on it. Terms like պատերազմ (war) or Ֆրանսիա (France) for instance are likely to be discovered within the document.

Some initial observations on the document :
- Image segmentation : there are a lot of different text blocks in the raw document, and distinguishing between them might be challenging. We will begin by concentrating on an isolated section of the text.
- Pre-processing : we will need to convert the image to black and white, enhance contrast, and employ denoising techniques to eliminate the verso background noise
- Font : the font used in this 1925 newspaper is likely unknown to Tesseract. However, according to tesseract-ocr/langdata/issues/67, the training data used a dozen fonts with italic and bold variations, so it should not be an issue
Using Tesseract
In this section, we examine the performance of Tesseract on our sample. We are using Tesseract 5.3.3 version on Windows (download page). The pytesseract module provides a python layer to call the Tesseract executables.
s a benchmark, we will use the following sample from the first page of the newspaper :

I wrote down the ground truth by hand :
Մեը հայրենակիցնեըէն շատերը շփոթութեան մէջ են ինքնու թեան թուղթերու, անցագրի ևն. մասին, մանաւանդ որ վերջերս նոր կարգագրութիւններ եղան:
which translates to (Google translate):
Many of our compatriots are confused about their own papers, passports, etc. about, especially since there were new regulations recently.
Not an Armenian speaker, but this looks plausible given the historical context.
Pre-processing
We try some brightness and contrast adjustments and measure the Character Error Rate (CER). CER measures how wrong our prediction is character by character, accounting for substitutions, insertions and deletions. The lower the better.
from PIL import Image, ImageEnhance
import pytesseract
from torchmetrics.text.cer import CharErrorRate
# Adjust image and call Tesseract
image = Image.open("sample.png").convert("L") # grayscale
image = ImageEnhance.Contrast(image).enhance(2.5)
image = ImageEnhance.Brightness(image).enhance(2.5)
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(image, lang="hye")
# Flatten into a single string before computing CER
predictions = " ".join(text.splitlines())
ground_truth = " ".join(open("sample.gt.txt", "r").read().splitlines())
cer = CharErrorRate()(predictions, ground_truth).item()
We observe that adjustments in contrast and brightness reduce the Character Error Rate (CER) to approximately 10-15%. The variance noticed in the CER could be attributed to the limited dataset size.
Augmenting the brightness aids in reducing the verso background noise. However, if it is increased excessively, certain shapes may begin to disappear, potentially leading to character confusion by Tesseract. This is particularly true for characters that only differ by a single stroke. At the moment, we will opt for a brightness setting of 2.5 and a contrast setting of 2.5. However, we remain aware that this could result in overfitting.
Sample image with contrast 2.5 and brightness 1.0, 2.5 and 3.0 :
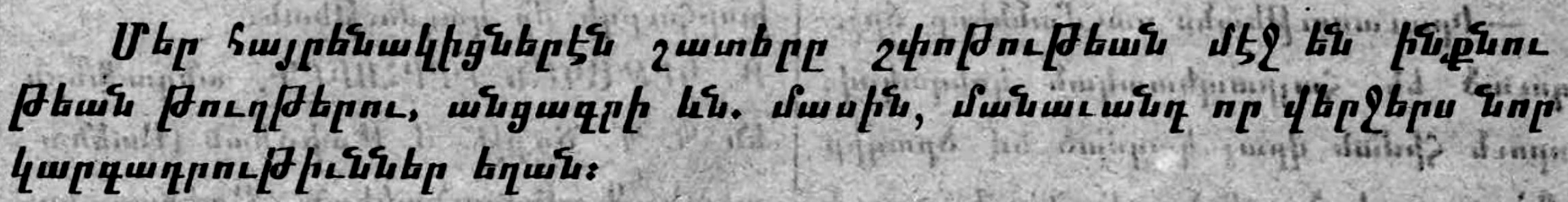
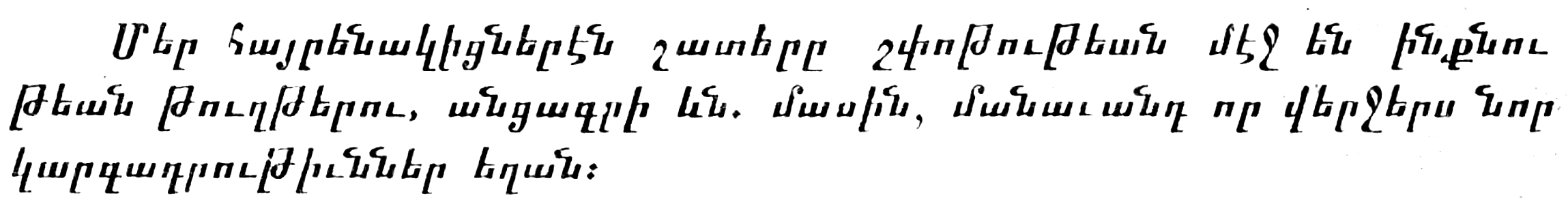
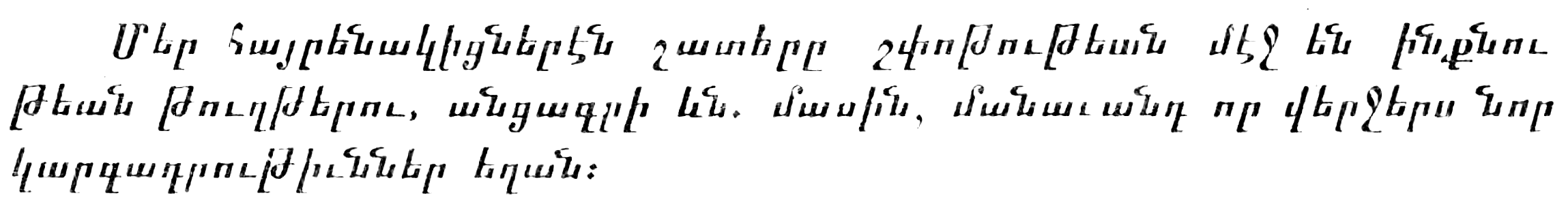
Results
The text extracted by Tesseract for our chosen image adjustment is
Բեր ձայրենակիցներեն չատերը շփոխութետն մէջ էն ինքնու թեան թԹուղն երու, անցագրի են. մասին, մանաւանդ որ վերջերս նոր կարդադրությիւններ եղան:
The CER is 13%, which is an character-level accuracy of 87%. Diffing the two texts (with difflib) line by line shows what went wrong :
- Մեը հայրենակիցնեըէն շատերը շփոթութեան մէջ են ինքնու
? ^ ^ ^ ^^ ^ ^ ^ ^
+ Բեր ձայրենակիցներեն չատերը շփոխութետն մէջ էն ինքնու
? ^ ^ ^ ^^ ^ ^ ^ ^
- թեան թուղթերու, անցագրի ևն. մասին, մանաւանդ որ վերջերս նոր
? ^ ^
+ թեան թԹուղն երու, անցագրի են. մասին, մանաւանդ որ վերջերս նոր
? + ^^ ^
- կարգագրութիւններ եղան:
? ^ ^
+ կարդադրությիւններ եղան:
? ^ ^ +
We can observe that errors occur when characters differ by just a single stroke, such as with ե and է or with ր and ը. The translation is notably far from the translated ground truth.
One realization that I had is that the serifs on է and ր can vary depending on the font. For instance, Courier New (a serif font) lacks a lower stroke on է but features lower strokes on ր. In contrast, a newspaper font possesses prominent lower strokes on ր, making it challenging to distinguish between ր and ը. The fonts used to train Tesseract appear to have a balanced representation of serif and sans-serif fonts. Training on a single font closely matching that of the newspaper could potentially yield better results.
I made an attempt to train Tesseract on the font Mk_Parz_U-Italic, which resembles the one used in newspapers. I used text2image to generate training examples (images and ground truth) from a Wikipedia article written in Armenian. However, I eventually encountered issues with tesstrain. I might consider retraining in the future.